11 KiB
Using Ultrafeeder with Grafana and Prometheus
Grafana is an analytics platform that can provide alternative graphs for readsb.
In this guide we will be using Prometheus as the data repository.
Using Grafana and Prometheus in this configuration does not require a plan, account, or credentials for their respective cloud offerings.
Ultrafeeder Image Tag
When using the :telegraf tag, the image contains Telegraf, which can be used to capture metrics from readsb if an output is enabled.
NOTE - READ CAREFULLY: As of 27 April 2023, the latest image no longer container Telegraf. If you want to send metrics to InfluxDB or Prometheus, please use the :telegraf tag like this in your docker-compose.yml file:
services:
tar1090:
image: ghcr.io/sdr-enthusiasts/docker-tar1090:telegraf
...
Hardware requirements
Prometheus will store a lot of data, and Grafana will do a lot of data queries. As a result, it would be better if you run these containers on a different system than your feeder Raspberry Pi. This will leave your Pi focused on data collection and processing, and unbothered by the CPU and Disk IO load that Prometheus/Grafana will cause.
You can do it on a single system. We're assuming below that you are not. If you do it on a single system, then you can combine the docker-compose.yml components in a single file
Step 1: Make Prometheus data available for the Ultrafeeder
- Edit your Ultrafeeder's
docker-compose.ymlfile and ensure that the following is set for theultrafeederservice:
environment:
- PROMETHEUS_ENABLE=true
- TAR1090_ENABLE_AC_DB=true
ports:
- 9273-9274:9273-9274
Now recreate the ultrafeeder container (docker-compose up -d ultrafeeder) and it will generate Prometheus data.
Step 2: create a container stack for prometheus and grafana
On the machine where you will run Prometheus and Grafana, create a docker-compose file in the /opt/grafana directory:
sudo mkdir -p -m777 /opt/grafana/grafana/appdata /opt/grafana/prometheus/config /opt/grafana/prometheus/data
cd /opt/grafana
cat > docker-compose.yml
Now paste in the following text *):
<‐‐ Click the arrow to see the docker-compose.yml text
version: '3.9'
volumes:
grafana:
driver: local
driver_opts:
type: none
device: "/opt/grafana/grafana/appdata"
o: bind
prom-config:
driver: local
driver_opts:
type: none
device: "/opt/grafana/prometheus/config"
o: bind
prom-data:
driver: local
driver_opts:
type: none
device: "/opt/grafana/prometheus/data"
o: bind
services:
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana-oss:latest
restart: unless-stopped
container_name: grafana
hostname: grafana
tty: true
# uncomment the following section and set the variables if you are exposing Grafana to the internet behind a rev web proxy:
environment:
# windrose panel plugin is needed for polar plots:
- GF_INSTALL_PLUGINS=snuids-radar-panel,fatcloud-windrose-panel
# uncomment and set the following variables if you are exposing Grafana to the internet behind a rev web proxy:
# - GF_SERVER_ROOT_URL=https://mywebsite.com/grafana/
# - GF_SERVER_SERVE_FROM_SUB_PATH=true
# The following variables are needed if you want to expose and embed any dashboards publicly:
# - GF_AUTH_ANONYMOUS_ENABLED=true
# - GF_AUTH_ANONYMOUS_ORG_NAME=public
# - GF_SECURITY_ALLOW_EMBEDDING=true
# - GF_PANELS_DISABLE_SANITIZE_HTML=true
# - GF_FEATURE_TOGGLES_ENABLE=publicDashboards
# The following variables will allow you to "share/render" dashboards as PNG graphics.
# You should also enabled the renderer container below.
# - GF_RENDERING_SERVER_URL=http://renderer:8081/render
# - GF_RENDERING_CALLBACK_URL=http://grafana:3000/
# - GF_LOG_FILTERS=rendering:debug
ports:
- 3000:3000
volumes:
- grafana:/var/lib/grafana
# The `renderer` container is needed if you want to share images of your dashboard as a graphic:
renderer:
image: grafana/grafana-image-renderer:latest
prometheus:
image: prom/prometheus
container_name: prometheus
hostname: prometheus
restart: unless-stopped
tmpfs:
- /tmp
volumes:
- prom-config:/etc/prometheus
- prom-data:/prometheus
ports:
- 9090:9090
*) The volume definition structure is written this way purposely to ensure that the containers can place files in the persistent directories. Do not try to "directly" map volumes (/opt/grafana/grafana/appdata:/var/lib/grafana).
You should be able to see the following directories:
/opt/grafana/grafana/appdata/opt/grafana/prometheus/config/opt/grafana/prometheus/data
Download and create Grafana and Prometheus for the first time with this command:
docker compose up -d
Step 3: Configuring Prometheus
Prometheus needs to be told where to look for the data from the ultrafeeder. We will create a target prometheus configuration file that does this, please copy and paste the following. Make sure to replace ip_xxxxxxx with the IP address or hostname of the machine where ultrafeeder is running:
docker exec -it prometheus sh -c "echo -e \" - job_name: 'ultrafeeder'\n static_configs:\n - targets: ['ip_xxxxxxx:9273', 'ip_xxxxxxx:9274']\" >> /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml"
docker stop prometheus
docker compose up -d
(If you screw this up, do NOT re-run the command. Instead, try sudo nano /opt/grafana//prometheus/config/prometheus.yml and fix it that way.)
Accessing Prometheus and Grafana via your browser
You should be able to point your web browser at:
http://docker.host.ip.addr:9090/to access theprometheusconsole.http://docker.host.ip.addr:3000/to access thegrafanaconsole, use admin/admin as initial credentials, you should be prompted to change the password on first login.
Remember to change docker.host.ip.addr to the IP address of your docker host.
Configuring data source and dashboard in Grafana
After you have logged into the grafana console the following manual steps are required to connect to prometheus as the data source
- Click
Add your first data sourcein the main panel - Click
Prometheusfrom the list of options provided - Input or select the following options, if the option is not listed, do not input anything for that option:
| Option | Input |
|---|---|
| Name | ultrafeeder |
| URL | http://prometheus:9090/ |
Clicking Save & Test should return a green message indicating success. The dashboard can now be imported with the following steps
- Hover over the
four squaresicon in the sidebar, click+ Import - Enter
18398into theImport via grafana.comsection and clickLoad - Select
ultrafeederfrom the bottom drop down list - Click
Importon the subsequent dialogue box
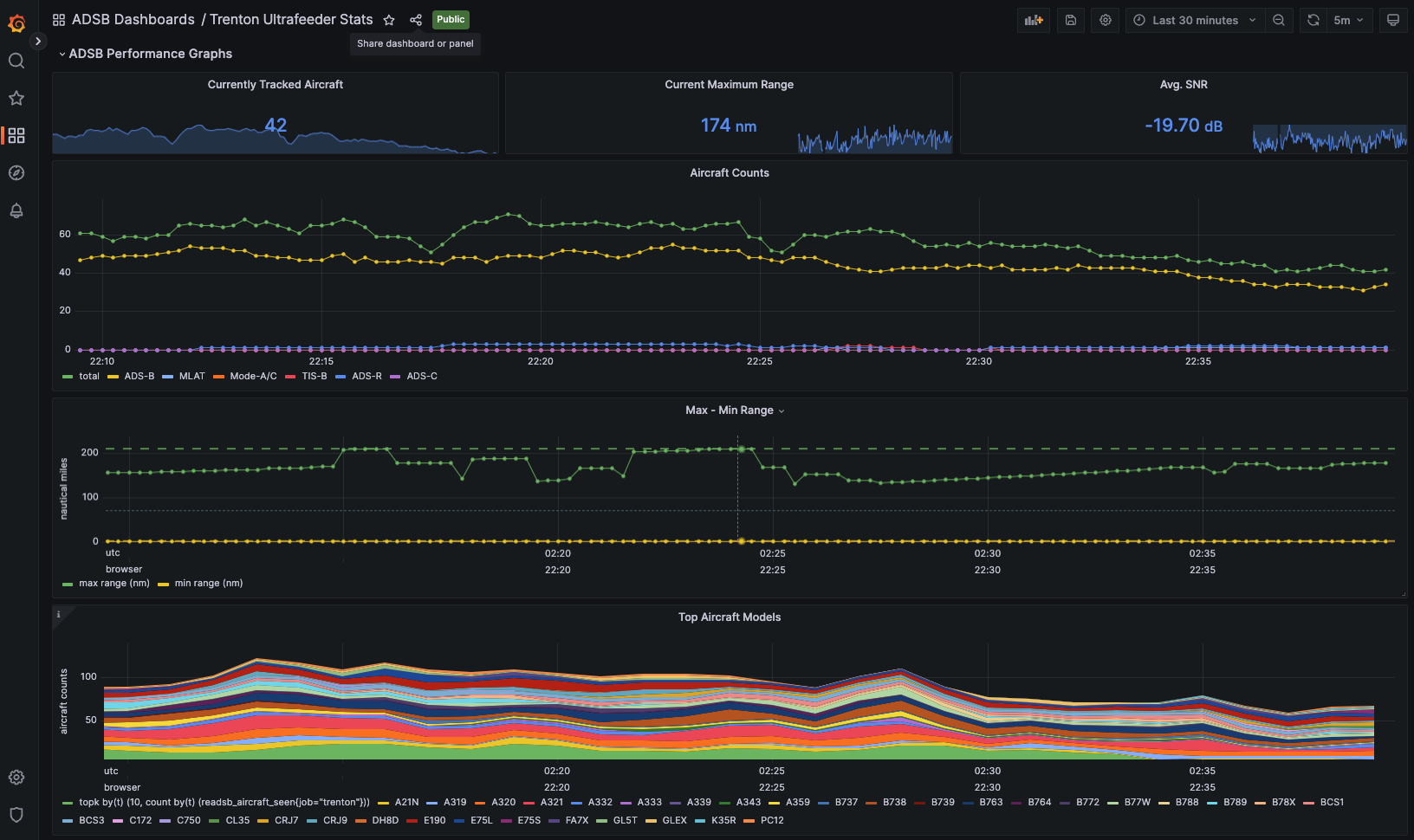
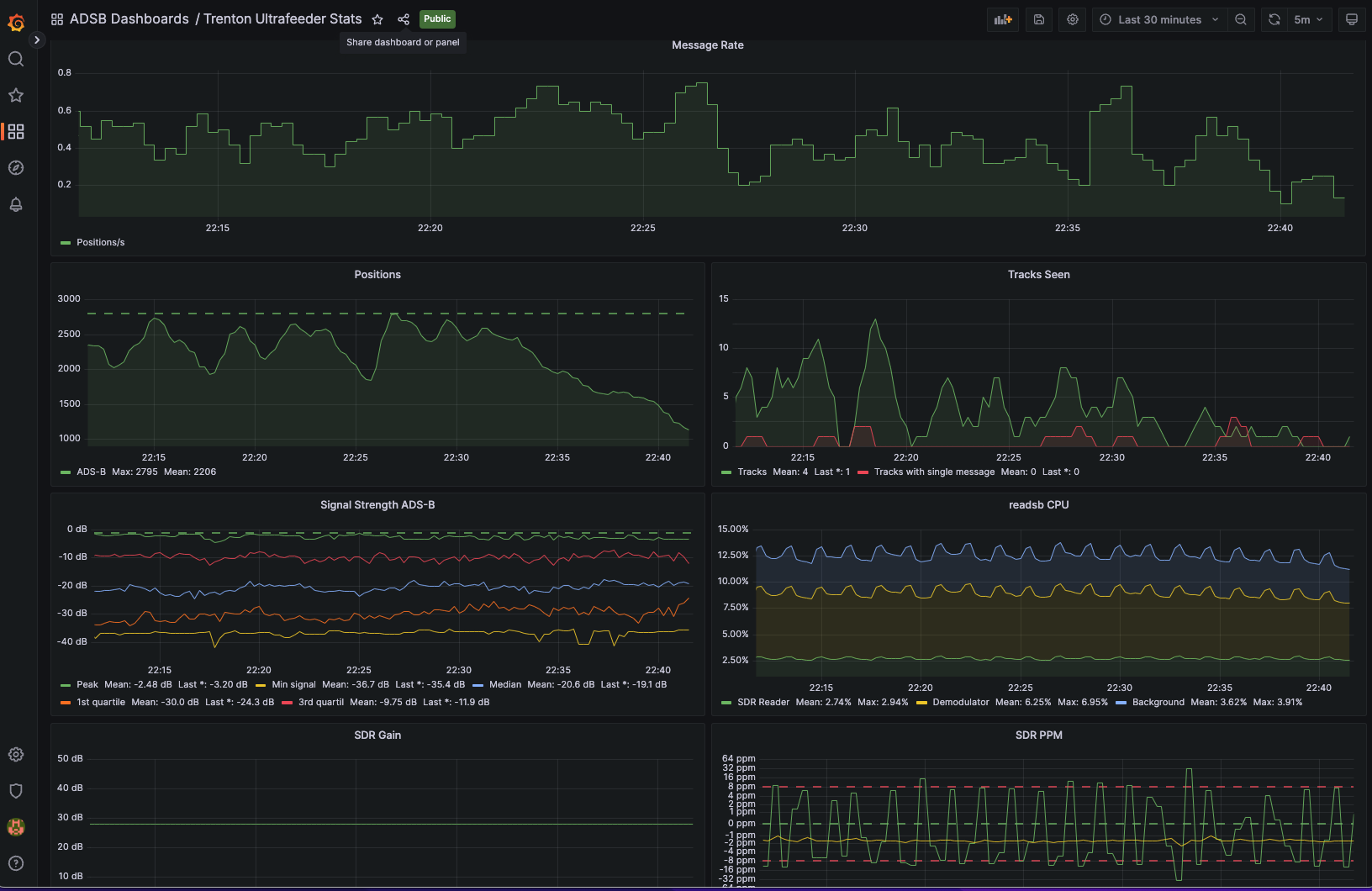
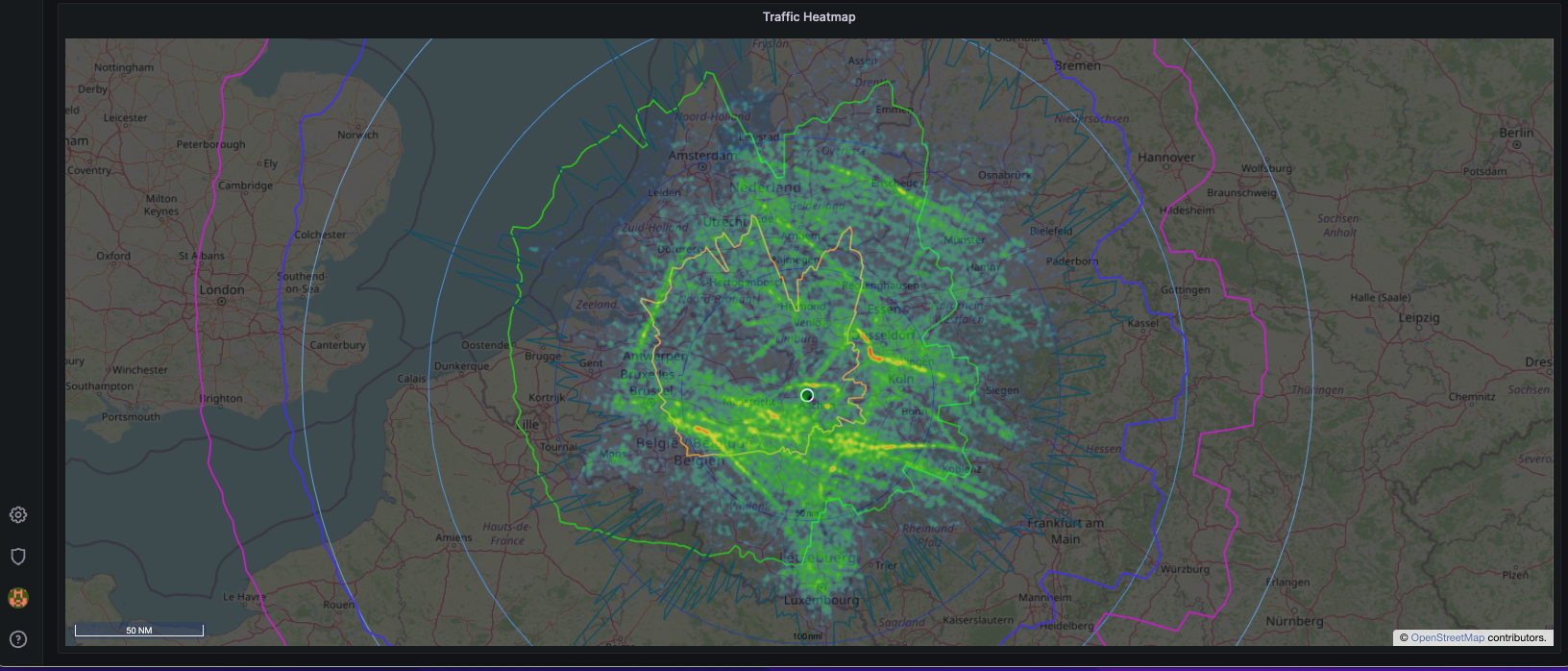
At this point you should see a very nice dashboard, you can find it under General in the Dashboards section.
Advanced Configuration: support for dashboards for multiple ultrafeeder instances
If you have multiple feeder stations with multiple instances of ultrafeeder, you can configure a dashboard for each of them. Here's how. In our example, we have two ultrafeeder instance called heerlen and trenton. You can adjust these names in accordance with your needs.
First execute all steps above, and then continue here.
Step 1: Edit your Prometheus config file so the job_names look like this
- job_name: 'heerlen'
static_configs:
- targets: ['10.0.0.100:9273', '10.0.0.100:9274']
- job_name: 'trenton'
static_configs:
- targets: ['10.0.0.101:9273', '10.0.0.101:9274']
Here, 10.0.0.100 is the IP address of the heerlen station, and 10.0.0.101 is the IP address of the trenton station. Yours will be different. Please keep the ports as you mapped them for Ultrafeeder in each instance. You should have a - job_name block for each ultrafeeder instance.
You can remove the ultrafeeder section as it will probably be a duplicate of what you just created.
Once you are done editing, restart Prometheus (docker restart prometheus).
Step 2: Change your initial Grafana dashboard to use the new job name
In the previous step, you replaced the ultrafeeder job name by two or more new names. Now, we need to create a copy of the dashboard for each of the job names and make sure they each use the data source from the correct ultrafeeder instance.
- Step 2a: Log into Grafana and open the Ultrafeeder dashboard that you already created
- Step 2b: Click on the cogwheel (
Dashboard Settings) in the top of the screen - Step 2c: Choose
JSON Modelfrom the Setting menu on the left of the screen and click anywhere in the JSON text - Step 2d. Press CTRL-F (Window/Linux) or CMD-F (Mac) and press the
>button to show Find and Replace: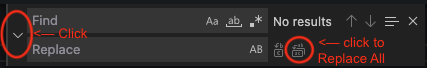
- Step 2e: Find all instances of
job=\"ultrafeeder\"and replace them withjob=\"heerlen\"(or whatever name your first feeder has) - Step 2f: Press
Save dashboardat the top right of the screen, followed bySaveon the next screen - Step 2g: Press ESC to go back to your dashboard
Now your first Grafana dashboard gets its data from the your first ultrafeeder instance.
Step 3: Clone the dashboard and repoint it at your second ultrafeeder instance
If you followed the steps above, you should be at your updated (first) dashboard. We'll now clone and adapt it for your second ultrafeeder instance:
- Step 3a: Press the
Shareicon (to the right of the star, next to the page title) - Step 3b: Click the
Exporttab. Switch onExport for sharing externally - Step 3c: Press
View JSONandCopy to Clipboard - Step 3d:
Xout of the popup box, leave the Dashboard, and go back to theBrowse Dashboardspage. - Step 3e: Click
New->Import. Right-click in theImport via panel jsonbox, and paste your clipboard. PressLoad - Step 3f: Change the
Nameanduid(pick anything you want), and selectPrometheusas data source. IMPORTANT: if you do not change theNameanduid, it will overwrite your existing dashboard. CHANGE BOTH OF THEM! Then pressImport - Step 3g: You will see your new dashboard, but it's still getting data from your first one. Follow steps 2b - 2g above to change the data source from
heerlen(or whatever you named it) totrenton(or whatever name you want to give to it)
Now you have 2 dashboards for 2 instances of Ultrafeeder!