mirror of
https://github.com/sdr-enthusiasts/docker-adsb-ultrafeeder.git
synced 2024-11-22 13:50:14 +00:00
276 lines
14 KiB
Markdown
276 lines
14 KiB
Markdown
# Using Ultrafeeder with Grafana and Prometheus
|
|
|
|
- [Using Ultrafeeder with Grafana and Prometheus](#using-ultrafeeder-with-grafana-and-prometheus)
|
|
- [Introduction](#introduction)
|
|
- [Ultrafeeder Image Tag](#ultrafeeder-image-tag)
|
|
- [Hardware requirements](#hardware-requirements)
|
|
- [Steps to install Prometheus, Grafana, and the Grafana Dashboard](#steps-to-install-prometheus-grafana-and-the-grafana-dashboard)
|
|
- [Step 1: Make Prometheus data available for the Ultrafeeder](#step-1-make-prometheus-data-available-for-the-ultrafeeder)
|
|
- [Step 2: create a container stack for `prometheus` and `grafana`](#step-2-create-a-container-stack-for-prometheus-and-grafana)
|
|
- [Step 3: Configuring Prometheus](#step-3-configuring-prometheus)
|
|
- [Accessing Prometheus and Grafana via your browser](#accessing-prometheus-and-grafana-via-your-browser)
|
|
- [Configuring data source and dashboard in Grafana](#configuring-data-source-and-dashboard-in-grafana)
|
|
- [Making the feeder's heatmap and graphs pages available in Grafana](#making-the-feeders-heatmap-and-graphs-pages-available-in-grafana)
|
|
- [Advanced Configuration: support for dashboards for multiple ultrafeeder instances](#advanced-configuration-support-for-dashboards-for-multiple-ultrafeeder-instances)
|
|
- [Step 1: Edit your Prometheus config file so the `job_name`s look like this](#step-1-edit-your-prometheus-config-file-so-the-job_names-look-like-this)
|
|
- [Step 2: Change your initial Grafana dashboard to use the new job name](#step-2-change-your-initial-grafana-dashboard-to-use-the-new-job-name)
|
|
- [Step 3: Clone the dashboard and repoint it at your second `ultrafeeder` instance](#step-3-clone-the-dashboard-and-repoint-it-at-your-second-ultrafeeder-instance)
|
|
|
|
## Introduction
|
|
|
|
[`Grafana`](https://grafana.com/) is an analytics platform that can provide alternative graphs for `readsb`.
|
|
|
|
In this guide we will be using [`Prometheus`](https://prometheus.io/) as the data repository.
|
|
|
|
Using Grafana and Prometheus in this configuration does not require a plan, account, or credentials for their respective cloud offerings.
|
|
|
|
## Ultrafeeder Image Tag
|
|
|
|
When using the `:telegraf` tag, the image contains [Telegraf](https://docs.influxdata.com/telegraf/), which can be used to capture metrics from `readsb` if an output is enabled.
|
|
|
|
**NOTE - READ CAREFULLY**: As of 27 April 2023, the `latest` image no longer contains Telegraf. If you want to send metrics to InfluxDB or Prometheus, please use the `:telegraf` tag like this in your `docker-compose.yml` file:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
services:
|
|
tar1090:
|
|
image: ghcr.io/sdr-enthusiasts/docker-tar1090:telegraf
|
|
...
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## Hardware requirements
|
|
|
|
Prometheus will store a lot of data, and Grafana will do a lot of data queries. As a result, it would be better if you run these containers on a different system than your feeder Raspberry Pi. This will leave your Pi focused on data collection and processing, and unbothered by the CPU and Disk IO load that Prometheus/Grafana will cause.
|
|
|
|
You *can* do it on a single system. We're assuming below that you are not. If you do it on a single system, then you can combine the `docker-compose.yml` components in a single file
|
|
|
|
## Steps to install Prometheus, Grafana, and the Grafana Dashboard
|
|
|
|
### Step 1: Make Prometheus data available for the Ultrafeeder
|
|
|
|
- Edit your Ultrafeeder's `docker-compose.yml` file and ensure that the following is set for the `ultrafeeder` service:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
environment:
|
|
- PROMETHEUS_ENABLE=true
|
|
- TAR1090_ENABLE_AC_DB=true
|
|
ports:
|
|
- 9273-9274:9273-9274
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Now recreate the ultrafeeder container (`docker-compose up -d ultrafeeder`) and it will generate Prometheus data.
|
|
|
|
### Step 2: create a container stack for `prometheus` and `grafana`
|
|
|
|
On the machine where you will run Prometheus and Grafana, create a docker-compose file in the `/opt/grafana` directory:
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
sudo mkdir -p -m777 /opt/grafana/grafana/appdata /opt/grafana/prometheus/config /opt/grafana/prometheus/data
|
|
cd /opt/grafana
|
|
cat > docker-compose.yml
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Now paste in the following text *):
|
|
|
|
<details>
|
|
<summary><‐‐ Click the arrow to see the <code>docker-compose.yml</code> text</summary>
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
version: '3.9'
|
|
|
|
volumes:
|
|
grafana:
|
|
driver: local
|
|
driver_opts:
|
|
type: none
|
|
device: "/opt/grafana/grafana/appdata"
|
|
o: bind
|
|
prom-config:
|
|
driver: local
|
|
driver_opts:
|
|
type: none
|
|
device: "/opt/grafana/prometheus/config"
|
|
o: bind
|
|
prom-data:
|
|
driver: local
|
|
driver_opts:
|
|
type: none
|
|
device: "/opt/grafana/prometheus/data"
|
|
o: bind
|
|
|
|
services:
|
|
grafana:
|
|
image: grafana/grafana-oss:latest
|
|
restart: unless-stopped
|
|
container_name: grafana
|
|
hostname: grafana
|
|
tty: true
|
|
# uncomment the following section and set the variables if you are exposing Grafana to the internet behind a rev web proxy:
|
|
environment:
|
|
# windrose panel plugin is needed for polar plots:
|
|
- GF_INSTALL_PLUGINS=snuids-radar-panel,fatcloud-windrose-panel
|
|
# uncomment and set the following variables if you are exposing Grafana to the internet behind a rev web proxy:
|
|
# - GF_SERVER_ROOT_URL=https://mywebsite.com/grafana/
|
|
# - GF_SERVER_SERVE_FROM_SUB_PATH=true
|
|
# The following variables are needed if you want to expose and embed any dashboards publicly:
|
|
# - GF_AUTH_ANONYMOUS_ENABLED=true
|
|
# - GF_AUTH_ANONYMOUS_ORG_NAME=public
|
|
# - GF_SECURITY_ALLOW_EMBEDDING=true
|
|
# - GF_PANELS_DISABLE_SANITIZE_HTML=true
|
|
# - GF_FEATURE_TOGGLES_ENABLE=publicDashboards
|
|
# The following variables will allow you to "share/render" dashboards as PNG graphics.
|
|
# You should also enabled the renderer container below.
|
|
# - GF_RENDERING_SERVER_URL=http://renderer:8081/render
|
|
# - GF_RENDERING_CALLBACK_URL=http://grafana:3000/
|
|
# - GF_LOG_FILTERS=rendering:debug
|
|
ports:
|
|
- 3000:3000
|
|
volumes:
|
|
- grafana:/var/lib/grafana
|
|
|
|
# The `renderer` container is needed if you want to share images of your dashboard as a graphic:
|
|
renderer:
|
|
image: grafana/grafana-image-renderer:latest
|
|
|
|
prometheus:
|
|
image: prom/prometheus
|
|
container_name: prometheus
|
|
hostname: prometheus
|
|
restart: unless-stopped
|
|
tmpfs:
|
|
- /tmp
|
|
volumes:
|
|
- prom-config:/etc/prometheus
|
|
- prom-data:/prometheus
|
|
ports:
|
|
- 9090:9090
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
</details>
|
|
|
|
*) The volume definition structure is written this way purposely to ensure that the containers can place files in the persistent directories. Do not try to "directly" map volumes (`/opt/grafana/grafana/appdata:/var/lib/grafana`).
|
|
|
|
You should be able to see the following directories:
|
|
|
|
- `/opt/grafana/grafana/appdata`
|
|
- `/opt/grafana/prometheus/config`
|
|
- `/opt/grafana/prometheus/data`
|
|
|
|
Download and create Grafana and Prometheus for the first time with this command:
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
docker compose up -d
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Step 3: Configuring Prometheus
|
|
|
|
Prometheus needs to be told where to look for the data from the ultrafeeder. We will create a target prometheus configuration file that does this, please copy and paste the following. Make sure to replace `ip_xxxxxxx` with the IP address or hostname of the machine where `ultrafeeder` is running:
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
docker exec -it prometheus sh -c "echo -e \" - job_name: 'ultrafeeder'\n static_configs:\n - targets: ['ip_xxxxxxx:9273', 'ip_xxxxxxx:9274']\" >> /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml"
|
|
docker stop prometheus
|
|
docker compose up -d
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
(If you screw this up, **do NOT** re-run the command. Instead, try `sudo nano /opt/grafana//prometheus/config/prometheus.yml` and fix it that way.)
|
|
|
|
### Accessing Prometheus and Grafana via your browser
|
|
|
|
You should be able to point your web browser at:
|
|
|
|
- `http://docker.host.ip.addr:9090/` to access the `prometheus` console.
|
|
- `http://docker.host.ip.addr:3000/` to access the `grafana` console, use admin/admin as initial credentials, you should be prompted to change the password on first login.
|
|
|
|
Remember to change `docker.host.ip.addr` to the IP address of your docker host.
|
|
|
|
### Configuring data source and dashboard in Grafana
|
|
|
|
After you have logged into the `grafana` console the following manual steps are required to connect to `prometheus` as the data source
|
|
|
|
1. Click `Add your first data source` in the main panel
|
|
2. Click `Prometheus` from the list of options provided
|
|
3. Input or select the following options, if the option is not listed, do not input anything for that option:
|
|
|
|
Option | Input
|
|
------------- | -------------
|
|
Name | ultrafeeder
|
|
URL | `http://prometheus:9090/`
|
|
|
|
Clicking `Save & Test` should return a green message indicating success. The dashboard can now be imported with the following steps:
|
|
|
|
1. Hover over the `four squares` icon in the sidebar, click `+ Import`
|
|
2. Enter `18398` into the `Import via grafana.com` section and click `Load`
|
|
3. Select `ultrafeeder` from the bottom drop down list
|
|
4. Click `Import` on the subsequent dialogue box
|
|
|
|
At this point you should see a very nice dashboard, you can find it under `General` in the `Dashboards` section.
|
|
|
|
### Making the feeder's heatmap and graphs pages available in Grafana
|
|
|
|
The dashboard comes preconfigured with panels that show the tar1090 heatmap and graphs1090 stats pages. These panels need to be configured to look for this data at the correct URL.
|
|
|
|
Note that these URLs need to be accessible from the browser that you use to see the Grafana dashboard - they should work if you enter them in your browser's URL box.
|
|
|
|
If you don't have access to these URLs, it'd be safe to simply delete these panels from your dashboard.
|
|
|
|
- Step a: Log into Grafana and open the Ultrafeeder dashboard that you already created
|
|
- Step b: Click on the cogwheel (`Dashboard Settings`) in the top of the screen
|
|
- Step c: Choose `JSON Model` from the Setting menu on the left of the screen and click anywhere in the JSON text
|
|
- Step d. Press CTRL-F (Window/Linux) or CMD-F (Mac) and press the `>` button to show Find and Replace:<br />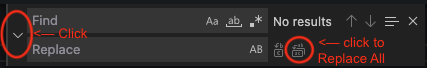
|
|
- Step e: Find all (2) instances of `my_feeder` and replace them with the IP of your tar1090 map page
|
|
- Step f: Press `Save dashboard` at the top right of the screen, followed by `Save` on the next screen
|
|
- Step g: Press ESC to go back to your dashboard
|
|
|
|
## Advanced Configuration: support for dashboards for multiple ultrafeeder instances
|
|
|
|
If you have multiple feeder stations with multiple instances of `ultrafeeder`, you can configure a dashboard for each of them. Here's how. In our example, we have two `ultrafeeder` instance called `heerlen` and `trenton`. You can adjust these names in accordance with your needs.
|
|
|
|
First execute all steps above, and then continue here.
|
|
|
|
### Step 1: Edit your Prometheus config file so the `job_name`s look like this
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
- job_name: 'heerlen'
|
|
static_configs:
|
|
- targets: ['10.0.0.100:9273', '10.0.0.100:9274']
|
|
- job_name: 'trenton'
|
|
static_configs:
|
|
- targets: ['10.0.0.101:9273', '10.0.0.101:9274']
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Here, `10.0.0.100` is the IP address of the `heerlen` station, and `10.0.0.101` is the IP address of the `trenton` station. Yours will be different. Please keep the ports as you mapped them for Ultrafeeder in each instance. You should have a `- job_name` block for each ultrafeeder instance.
|
|
|
|
You can remove the `ultrafeeder` section as it will probably be a duplicate of what you just created.
|
|
|
|
Once you are done editing, restart Prometheus (`docker restart prometheus`).
|
|
|
|
### Step 2: Change your initial Grafana dashboard to use the new job name
|
|
|
|
In the previous step, you replaced the `ultrafeeder` job name by two or more new names. Now, we need to create a copy of the dashboard for each of the job names and make sure they each use the data source from the correct `ultrafeeder` instance.
|
|
|
|
- Step 2a: Log into Grafana and open the Ultrafeeder dashboard that you already created
|
|
- Step 2b: Click on the cogwheel (`Dashboard Settings`) in the top of the screen
|
|
- Step 2c: Choose `JSON Model` from the Setting menu on the left of the screen and click anywhere in the JSON text
|
|
- Step 2d. Press CTRL-F (Window/Linux) or CMD-F (Mac) and press the `>` button to show Find and Replace:<br />
|
|
- Step 2e: Find all instances of `job=\"ultrafeeder\"` and replace them with `job=\"heerlen\"` (or whatever name your first feeder has)
|
|
- Step 2f: Press `Save dashboard` at the top right of the screen, followed by `Save` on the next screen
|
|
- Step 2g: Press ESC to go back to your dashboard
|
|
|
|
Now your first Grafana dashboard gets its data from the your first `ultrafeeder` instance.
|
|
|
|
### Step 3: Clone the dashboard and repoint it at your second `ultrafeeder` instance
|
|
|
|
If you followed the steps above, you should be at your updated (first) dashboard. We'll now clone and adapt it for your second `ultrafeeder` instance:
|
|
|
|
- Step 3a: Press the `Share` icon (to the right of the star, next to the page title)
|
|
- Step 3b: Click the `Export` tab. Switch on `Export for sharing externally`
|
|
- Step 3c: Press `View JSON` and `Copy to Clipboard`
|
|
- Step 3d: `X` out of the popup box, leave the Dashboard, and go back to the `Browse Dashboards` page.
|
|
- Step 3e: Click `New` -> `Import`. Right-click in the `Import via panel json` box, and paste your clipboard. Press `Load`
|
|
- Step 3f: Change the `Name` and `uid` (pick anything you want), and select `Prometheus` as data source. IMPORTANT: if you do not change the `Name` and `uid`, it will overwrite your existing dashboard. CHANGE BOTH OF THEM! Then press `Import`
|
|
- Step 3g: You will see your new dashboard, but it's still getting data from your first one. Follow steps 2b - 2g above to change the data source from `heerlen` (or whatever you named it) to `trenton` (or whatever name you want to give to it)
|
|
|
|
Now you have 2 dashboards for 2 instances of Ultrafeeder!
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|