6.3 KiB
Using Ultrafeeder with Grafana and Prometheus
Grafana is an analytics platform that can provide alternative graphs for readsb.
In this guide we will be using Prometheus as the data repository.
Using Grafana and Prometheus in this configuration does not require a plan, account, or credentials for their respective cloud offerings.
Hardware requirements
Prometheus will store a lot of data, and Grafana will do a lot of data queries. As a result, it would be better if you run these containers on a different system than your feeder Raspberry Pi. This will leave your Pi focused on data collection and processing, and unbothered by the CPU and Disk IO load that Prometheus/Grafana will cause.
You can do it on a single system. We're assuming below that you are not. If you do it on a single system, then you can combine the docker-compose.yml components in a single file
Step 1: Make Prometheus data available for the Ultrafeeder
- Edit your Ultrafeeder's
docker-compose.ymlfile and ensure that the following is set for theultrafeederservice:
environment:
- PROMETHEUS_ENABLE=true
ports:
- 9273-9274:9273-9274
Now recreate the ultrafeeder container (docker-compose up -d ultrafeeder) and it will generate Prometheus data.
Step 2: create a container stack for prometheus and grafana
On the machine where you will run Prometheus and Grafana, create a docker-compose file in the /opt/grafana directory:
mkdir -p -m777 /opt/grafana && cd /opt/grafana
cat > docker-compose.yml
Now paste in the following text:
<‐‐ Click the arrow to see the docker-compose.yml text
version: '3.9'
services:
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana-oss:latest
restart: unless-stopped
container_name: grafana
hostname: grafana
tty: true
# uncomment the following section and set the variables if you are exposing Grafana to the internet behind a rev web proxy:
# environment:
# - GF_SERVER_ROOT_URL=https://mywebsite.com/grafana
# - GF_SERVER_SERVE_FROM_SUB_PATH=true
ports:
- 3000:3000
volumes:
- /opt/grafana/grafana/appdata:/var/lib/grafana
prometheus:
image: prom/prometheus
container_name: prometheus
hostname: prometheus
restart: unless-stopped
tmpfs:
- /tmp
volumes:
- /opt/grafana/prometheus/config:/etc/prometheus
- /opt/grafana/prometheus/data:/prometheus
ports:
- 9090:9090
Once you have created and saved this docker-compose.yml file, give these commands to create the mapped volumes:
docker compose up -d
docker compose stop prometheus
docker compose stop grafana
Now, you should be able to see the following directories:
/opt/grafana/grafana/appdata/opt/grafana/prometheus/config/opt/grafana/prometheus/data
Step 3: Configuring Prometheus
Prometheus needs to be told where to look for the data from the ultrafeeder. We will create a target prometheus configuration file that does this, please copy and paste the following:
<‐‐ Click the arrow to see the shell script
sudo touch /opt/grafana/prometheus/config/prometheus.yml
sudo chmod a+rwx /opt/grafana/prometheus/config/prometheus.yml
cat > /opt/grafana/prometheus/config/prometheus.yml <<EOF
global:
scrape_interval: 15s # Set the scrape interval to every 15 seconds. Default is every 1 minute.
evaluation_interval: 15s # Evaluate rules every 15 seconds. The default is every 1 minute.
alerting:
alertmanagers:
- static_configs:
- targets:
rule_files:
scrape_configs:
# The job name is added as a label `job=<job_name>` to any timeseries scraped from this config.
- job_name: "prometheus"
static_configs:
- targets: ["localhost:9090"]
- job_name: 'readsb'
static_configs:
- targets: ['ip_of_ultrafeeder_machine:9273', 'ip_of_ultrafeeder_machine:9274']
EOF
Make sure to change ip_of_ultrafeeder_machine to the IP address or hostname of your ultrafeeder machine.
Once the file has been updated, issue the command docker compose up -d in the application directory to apply the changes and bring up the prometheus and grafana containers.
At this point we will need to add a collector definition to prometheus and restart with the new configuration.
- Issue the command
docker exec -it prometheus sh -c "echo -e \" - job_name: 'readsb'\n static_configs:\n - targets: ['readsb:9273']\" >> /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml" - Issue the command
docker stop prometheus - Issue the command
docker compose up -d
You should also be able to point your web browser at:
http://docker.host.ip.addr:9090/to access theprometheusconsole.http://docker.host.ip.addr:3000/to access thegrafanaconsole, use admin/admin as initial credentials, you should be prompted to change the password on first login.
Remember to change docker.host.ip.addr to the IP address of your docker host.
Configuring data source and dashboard in Grafana
After you have logged into the grafana console the following manual steps are required to connect to prometheus as the data source
- Click
Add your first data sourcein the main panel - Click
Prometheusfrom the list of options provided - Input or select the following options, if the option is not listed, do not input anything for that option:
| Option | Input |
|---|---|
| Name | readsb |
| URL | http://prometheus:9090/ |
Clicking Save & Test should return a green message indicating success. The dashboard can now be imported with the following steps
- Hover over the
four squaresicon in the sidebar, click+ Import - Enter
18398into theImport via grafana.comsection and clickLoad - Select
readsbfrom the bottom drop down list - Click
Importon the subsequent dialogue box
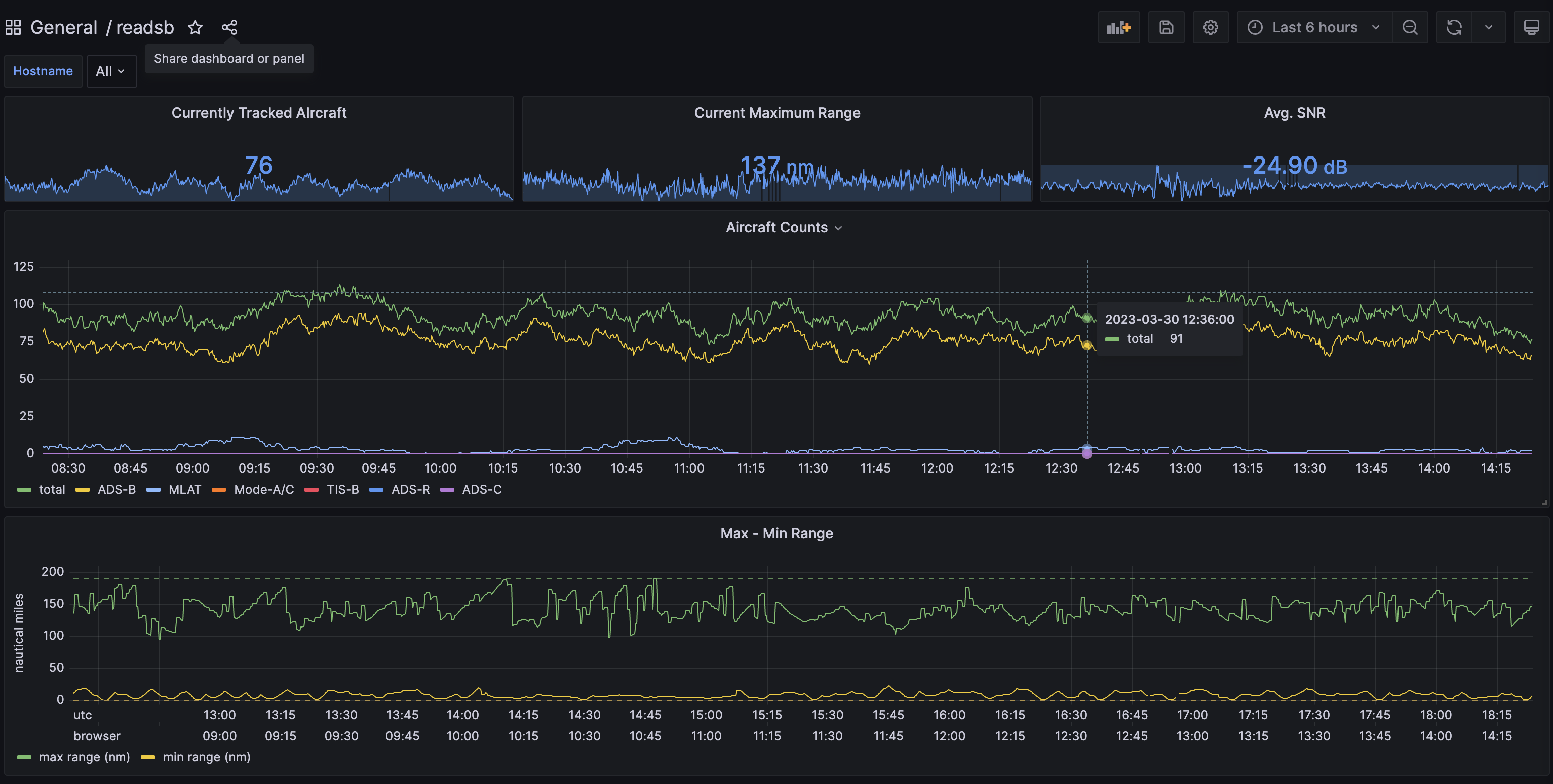
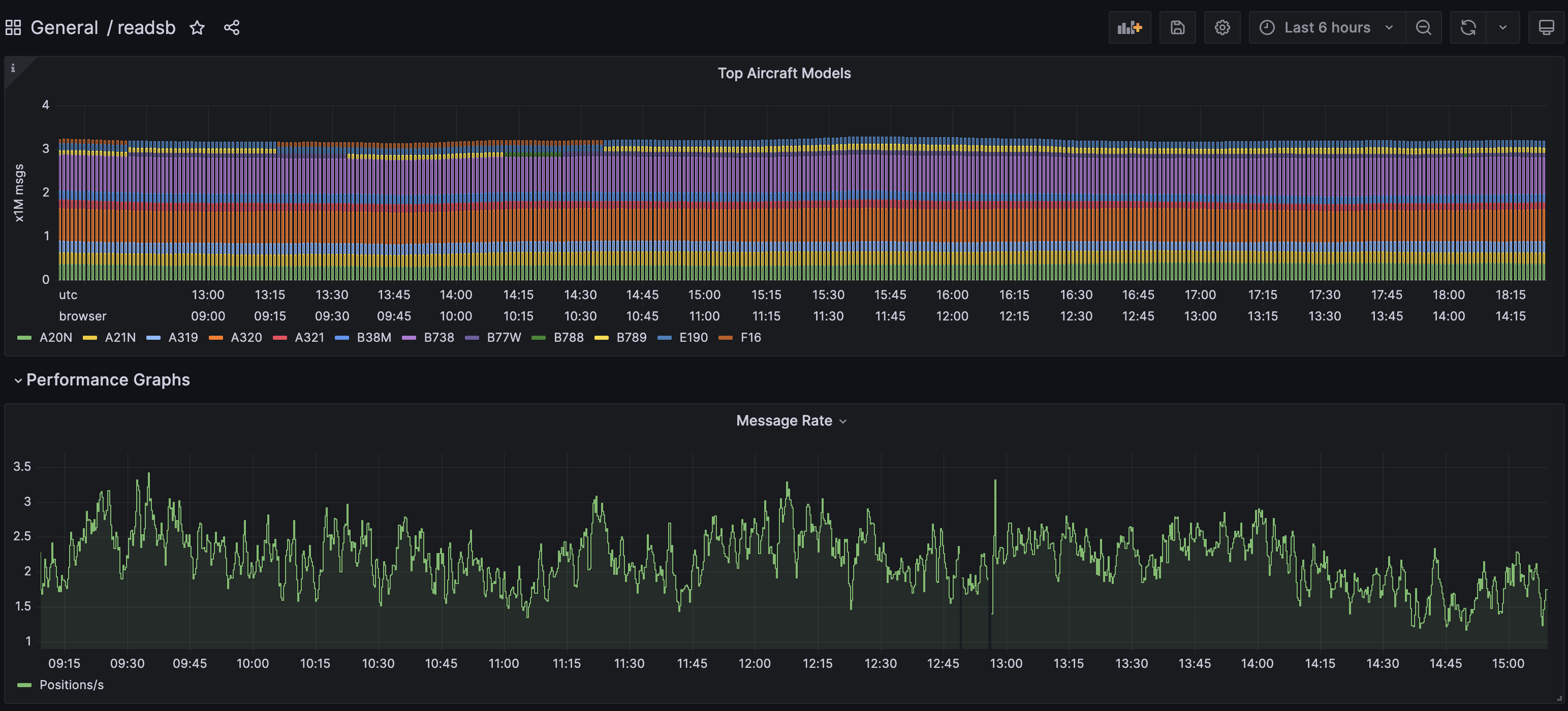
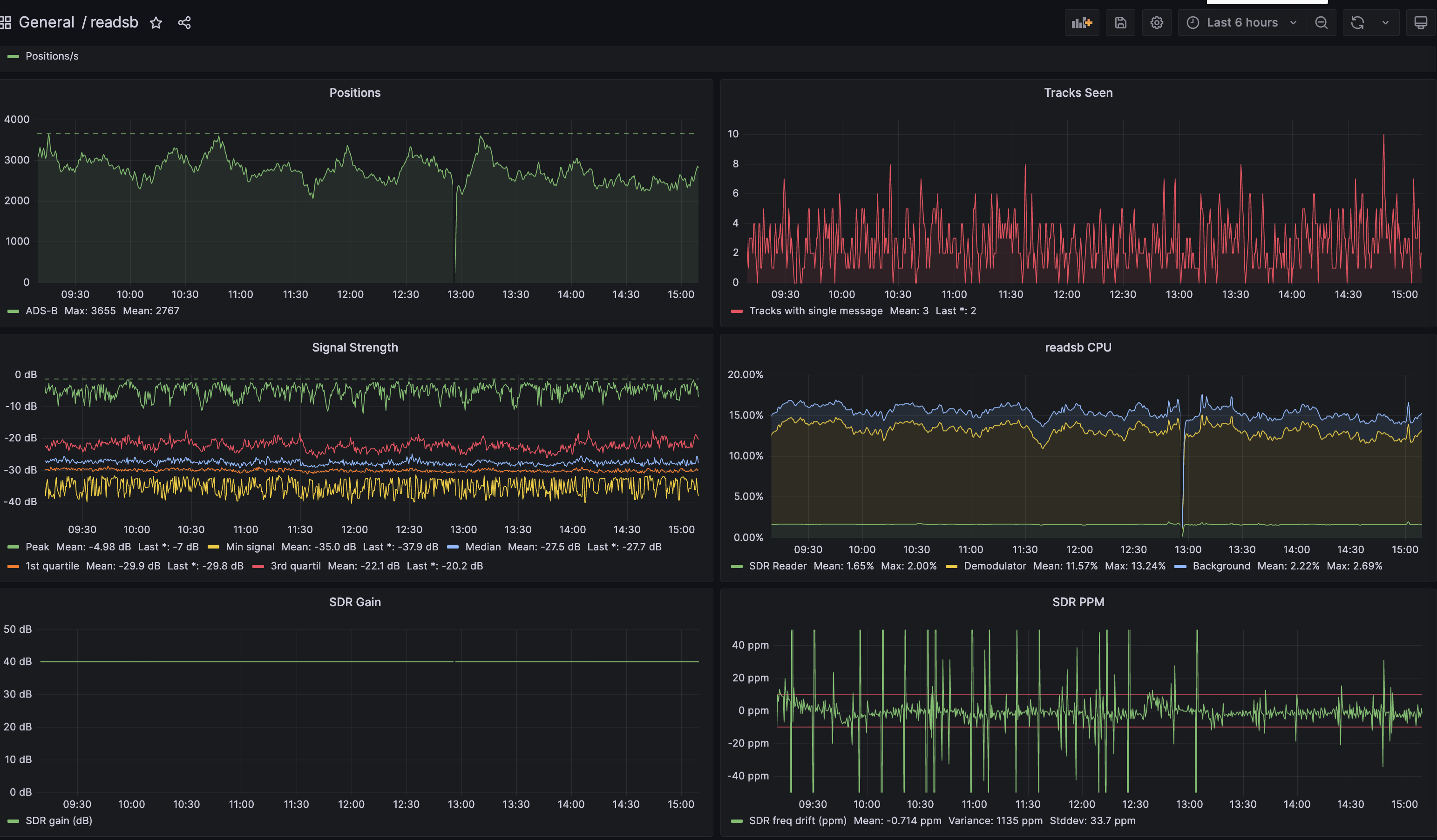
At this point you should see a very nice dashboard, you can find it under General in the Dashboards section.